
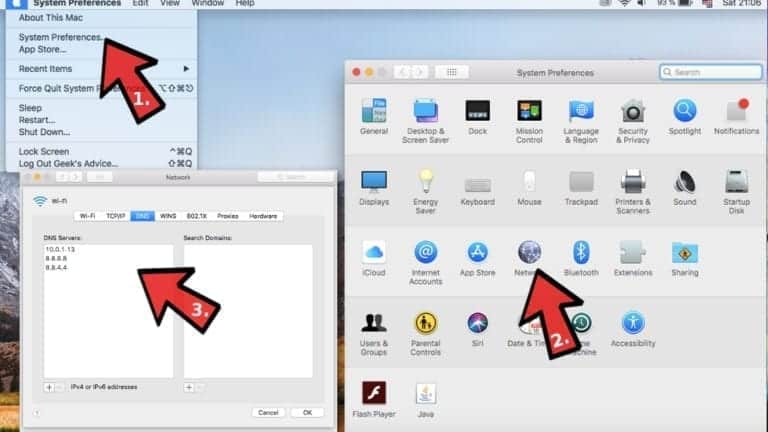

If a machine has recently visited the page it wants to access, the cache can supply the IP address of its web server, completing the website request before the lookup has to query the DNS server. In turn, the operating system (OS) uses caching to store DNS resource records, which avoids redundancy when attempting to access a web page and therefore decreases DNS lookup latency. As a whole, the DNS translates domain names, a verbal nomenclature humans can more easily understand and recall, to the numerical naming and transmission method required by computers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
